What is Product Management?

What is Product Management?
Product management supports and manages all activities of a product’s life cycle from market analysis to development, positioning, product launch, and marketing. The goal of a product manager is to analyze and understand the customers and develop a solution that not just solves the problem, but exceeds the customer’s expectations.
Martin Eriksson defines product management as “the intersection between business, technology, and user experience”.
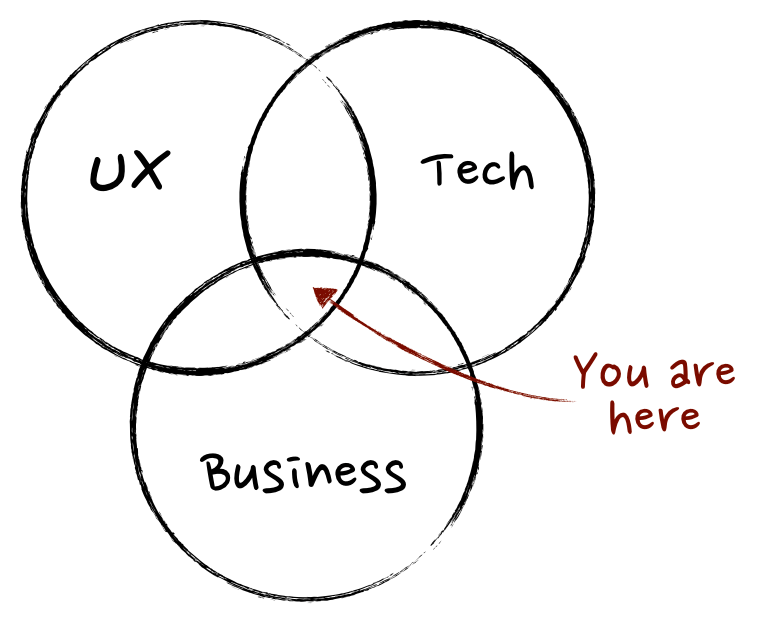

Source: Martin Eriksson
Business – The product manager focuses on how to optimize the product and how to maximize the business value from this. To achieve this, he has to close the communication gap between developers, customers, and business.
UX – Product managers focus on the user experience and the relationship between user and company. He represents the customers inside the company. This means that he tests the product, talks to customers to get feedback, and works closely together with the UX designers’ development team.
Technology – A product manager doesn’t have to be a developer but to make the right decisions he has to understand how a product gets built and how the technology works. This is especially important in agile projects where the product manager spends most of the time with the development team.
“The job of a product manager is to discover a product that is valuable, usable, and feasible.” – Marty Cagan
What are the jobs of a Product Manager?
Product management is an organizational function that supports and manages all activities of a product’s life cycle from market analysis to development, positioning, product launch, and marketing.
The goal of product management is to analyze and understand the customers and develop a solution that not just solves the problems but exceeds the customer’s expectations.
A product manager generally focuses on the following core responsibilities:
Research: To gain relevant information, the product manager defines, personas, and analyzes the market and competitors.
Strategy: The relevant information gets shaped into a high-level strategic plan for the product. The strategy includes goals, an overview of the product, prioritization of features, and a rough timeline. Typically, product managers use a product roadmap to develop the strategy.
Communication: Communication includes cross-functional leadership. The strategy gets presented to key stakeholders across the complete organization e.g. executives, investors and the development, marketing, and sales teams. These product professionals communicate during the development process and beyond.
Coordinating Development: After accepting the strategy the plan has to be realized. During the realization, the product manager coordinates the relevant teams like development, marketing and sales team.
Feedback and Data Analysis: After the product is built, tested, and introduced to the market, the product manager will analyze data and learn from user feedback. It is the goal to find out what worked, what didn’t work, and what should change. This analysis and feedback will be implemented into further iterations of the product.
Inbound vs. Outbound Product Management
Setting up the strategy and defining the roadmap is often considered to be inbound word whereas bringing the product to the market is often considered to be outbound. A great product manager has a set of skills to do both parts of product management.
Both parts can be performed by one product manager or two managers who work closely together. For a successful product, it is important to synchronize both parts of product management.
Inbound Product Management (Product Development)
Make sure that the developed product meets the demands of the customers, solves the right problems, and is cost-effective. It involves tasks like doing market research, setting up a strategy, and managing the product roadmap as well as coordinating the development.
Outbound Product Management (Product Marketing)
Includes product marketing, customer communication, product launch, advertising, PR, and events. They educate the market about the product and analyze the feedback from the customers.
Why is Product Management important?
In our article about product management statistics, we gathered interesting stats about the importance of product management.
For example, a fully optimized product manager can increase company profits by 34.2%”.
Product Managers also are important because they measure the success of their products and take responsibility for it.
Conclusion
Martin Eriksson answers the question “What is Product Management?” with “the intersection between business, technology, and user experience”.
Product Management can be separated into Product Development and Product Marketing. These two parts go hand in hand and are often run by one product manager.
Related Articles:
AUTHOR
Annemarie Bufe
Product Analytics Expert
Passionate hobby dancer. Working at UXCam.

Related articles
Tool Comparisons
UXCam vs Amplitude: A real comparison for mobile product analytics
Compare UXCam and Amplitude for mobile product analytics. See where event-based metrics work, where they fall short, and how UXCam's AI-powered product analytics platform reveals what's actually happening in your...

Begüm Aykut
Growth Marketing Manager
Product best practices
App Onboarding Guide: Top 10 Onboarding Flow Examples 2026
Take a look at 10 examples of apps that get user onboarding flows right. Get inspired by proven app onboarding approaches and improve your...

Jonas Kurzweg
Product Analytics Expert
App Analytics
Mobile App Tracking: Practical Guide & Best Tools [2026]
The best tracking tools for mobile...

Jonas Kurzweg
Product Analytics Expert

