User-Centered Design - Definition, Benefits & Methods
PUBLISHED
23 June, 2024


It’s been a couple of weeks since your team celebrated the release of a new search feature on your mobile app. Your dashboards are populating, and it dawns on you that no one is using the feature. Not only that but simultaneously, the app store reviews are rolling with complaints about the latest release and its negative effect on their user experience.
If this sounds like a recurring nightmare, it might be time to question your user experience design and development processes. Are you truly putting your customer first?
Building a product that users love is not as easy as it sounds, especially if you have a timeline and budget to stick to. However, in today's fast-paced world of Amazon and Uber, customers have high expectations for the software, websites, and apps they use.
70% of online businesses that fail do so because of bad usability, and 68% of users give up on a brand if they think it doesn't care about them.
User-Centered Design (UCD) offers a fresh approach for product managers and designers who are determined to build only the best experiences for their users. Top brands genuinely live and breathe the voice of their customer and use insights to build products their users love.
In this guide, you will learn about the art and science of listening to your users and solving their problems in a meaningful way.
What is User-Centered Design?
User-centered design (sometimes called user-centric design) is a highly customer-centric approach to building and developing products. Sometimes referred to as human-centered design, it is more than a design process - it is both a philosophy and a framework.
It means putting the needs and desires of your customers at the center of everything you do to create ideal user experiences.
User-centric design requires a solid understanding of who your customers are and what they need. It might sound obvious, but teams often lack a deep, nuanced understanding of who their customers are and where product-market fit is strongest.

User-centric design asks questions like, what problems are worth solving? What kind of solution could help? With user profiles and psychographics, it taps into users' psychology and emotional background to understand their needs and desires on a deeper level. At the same time, you need to drive business value and balance your company goals, priorities, and resources alongside users' needs.
UX Designers and product managers who use the UCD methodologies know they need the right data to understand user needs. This typically involves extensive research, surveys, user testing, and tools such as UXCam to gain insight into user behavior.
Ultimately, user-centered design is an asset to any company. It enables you to build and ship products that provide significant and long-term value to the user - the kind of products people fall in love with and tell their friends about.
Why is User-Centered Design important?
User-centered design is important because it leads to superior usability - and these days, user experience (UX) is a business advantage.
With user profiles and psychographics, it taps into users' psychology and emotional background to understand their needs and desires on a deeper level.
Your customers might not have heard of user-focused design, but they almost certainly prefer to buy products that are easy to use and navigate and solve a problem.
Users should not have to change their behaviors or expectations to fit your product. Understanding their needs and building a product around it can make the difference between a great user experience and a frustrating failure.
User-Centered Design offers many benefits, including:
Avoid user frustration
Streamline the development process
Increase ROI
Enhance competitiveness
In today's competitive business landscape, brands that don't put their customers first are at risk of falling behind. User-oriented design plays a key role in helping you achieve your business goals, such as increased sales, improved customer satisfaction, and higher customer retention.
Mobile App Product Management Certification
If you are reading this blog post, you want to improve your product management skills. We have created a course to help you do just that:
Step-by-step guide with over 15 templates and frameworks
Free certification
Content is based on expert interviews
Certification document for your resume and LinkedIn profile
Become a certified mobile app product manager for free here.
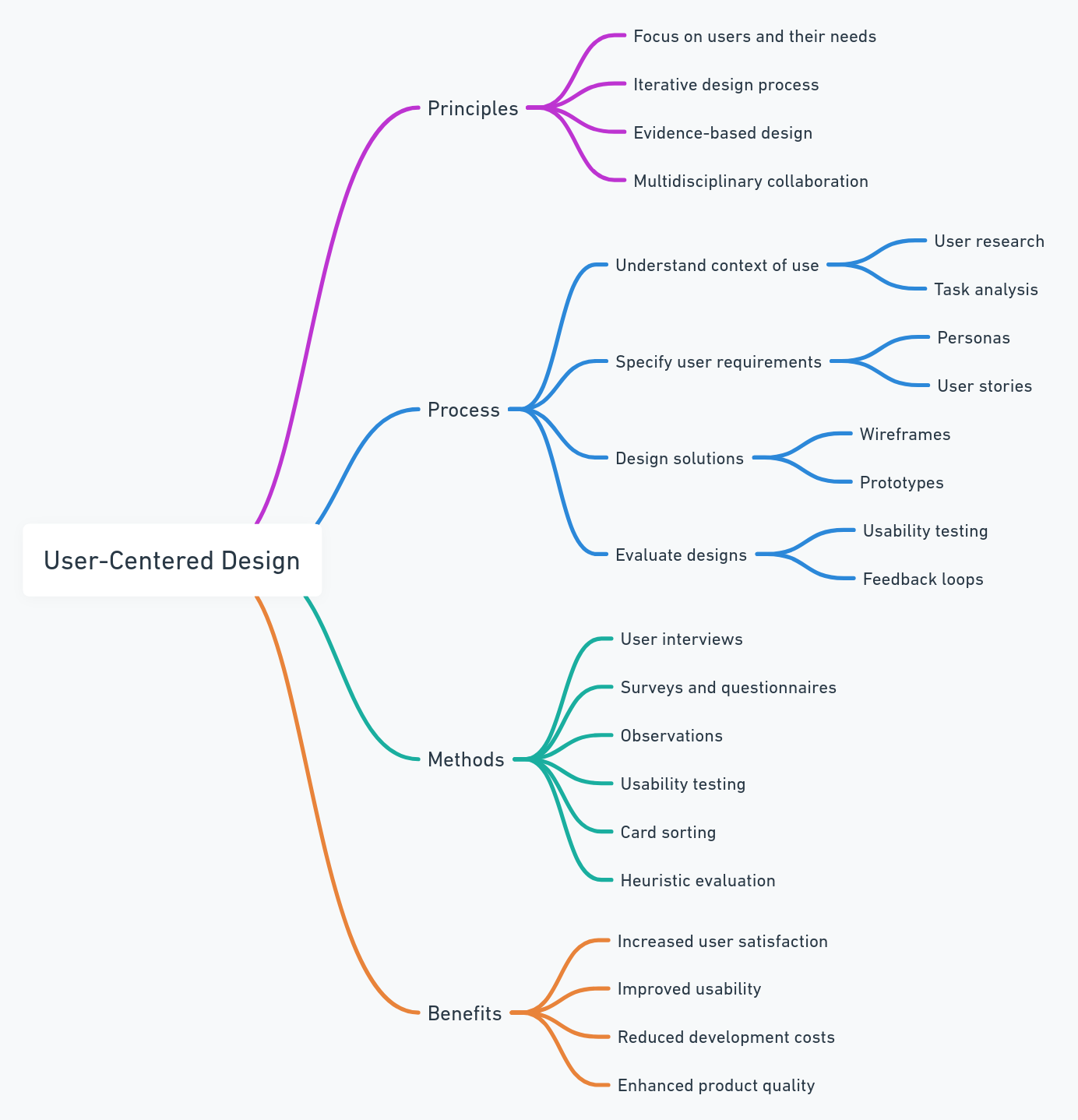
User-Centered Design Principles
Before jumping into the specific steps of a UCD process, a solid understanding of the User-Centered Design principles is vital. We have identified eight UCD principles that are the backbone of a successful design strategy. Without these, you will struggle to implement a user-centered design successfully, and it may not even truly be a user-centric design. So, let's dive in.
Product vision and impact
Above all else, you need an inspiring vision for your brand. This vision is the "north star" for your team and your product. What does your brand stand for? What problem do you solve for your users? Why should they come to you? These fundamental questions are a key part of your brand identity. This piece of the puzzle needs to be solved before you start building or even talking about features and benefits.
Understand your customers
To be successful, a business needs to align with the needs of its customers. People come to you because they need something. This is usually because you solve a problem they are facing or fulfill a desire they have.
Businesses should use qualitative and quantitative data to paint a full picture of user needs and behavior. These days, you have an abundance of options available at your fingertips. Popular research methods include surveys, user testing tools, and user analytics platforms such as UXCam.
Choose the most significant opportunity
User needs are complex and near-infinite. Most design or development teams will tell you they have a long development backlog. Making their way through everything on the list of desired features or suggested design changes would be near impossible. That means you need to prioritize. But how can you decide what is a must-have and what is merely nice-to-have?
In User-Centered Design, prioritization is based on the expected impact. Pick a specific opportunity space or problem to solve where the need and business value are most significant, then synthesize the research into UX design challenges.
Measure success through outcomes
Ultimately, it's about impact, not output. Even today, many businesses are still stuck in the old way of measuring how many features they shipped and how many hours they spent on development time.
We aim to drive our business goals by serving our users in user-oriented design. The goal is not to build more features but to positively influence user behavior by better meeting our customers' needs. We also move the needle on our business and financial KPIs when we do this.
Collaborate to innovate
A user-centered approach to product design is highly collaborative. It starts with ideation as part of a team. Together, you select design challenges to pursue through collaborative design thinking and framing.
Designers, product managers, and UCD experts can share ideas, analyze a feature or issue from various angles, and suggest different solutions. A team benefits from the strengths of their peers and can learn from each other.
User-centered design is not something you can effectively do on your own. It works best when teams come together to share their best ideas and deliver on them.
Create hypotheses
Acting on assumptions is risky. Let's say you think your users need X or don't like Y. You could be right - on the other hand, you might have misinterpreted their behavior or misunderstood their needs.
Before building anything or taking any tangible action, frame your assumption as a hypothesis. This hypothesis should connect to desired outcomes and solutions, which will help you to check relevant KPIs and measure the potential impact later.
Test and validate
Testing is not just a single step of the UDC process. It is an ongoing activity that happens before, during, and after you are working on a solution.
It is highly recommended to evaluate design decisions through usability testing and analytics platforms, such as UXCam, that provide data and insights into user behavior.
Prototyping and testing your ideas to evaluate your hypothesis will help you scrap bad ideas before you ship them, double down on key focus areas, and give you and your team confidence that you are headed in the right direction. Testing also increases your credibility internally, as other teams and managers see you have a business justification for your design projects.
Iterate based on data
UCD is a highly data-driven and iterative design process. It is not enough to bring out a new release and hope for the best. When you release a new product or feature, track and measure the impact on user behavior and keep an eye on the associated business metrics.
World-class UX design teams and product managers are diligent about measuring the impact of what they have delivered, and they take action based on the data when needed.
For instance, you might release a slick new design of your User Interface (UI) and then realize users now take longer to accomplish a task, the completion rate for certain user flows has decreased, or users are using the search function more because they cannot find what they are looking for. Even if the data shows that your new design has enhanced the user experience, there is always room for further improvement.
In both cases, it is important to monitor user behavior, analyze the data, and take action when needed.
What is the User Centered Design (UCD) Process Like?

User Centered Design process is a cycle that flows smoothly to create first-class products with every release. Let's dive into the UCD process and how the individual steps come together to enable you to build and ship customer-centric products.
1. Generative Research
Gain a deep understanding of your users by empathizing with them. Interview them to learn about the context of their daily lives, goals, motivations, and problems, including the areas where your product might be involved. Analyze and synthesize into personas that represent a general portrait of your users.
2. Ideation
Ideation is a key part of the UCD process. In your initial brainstorming sessions, you will identify the personas who will use the product or feature, the purpose they will use it for and the circumstances under which they will use it. Afterward, you can use data to refine your user scenarios and flesh out use cases.
3. Outline business requirements
The next step is to specify the business requirements and user goals that must be met for the product to be successful.
4. Conceptualization and prototyping
Now, it is time to start creating real design solutions. This involves starting with a general design concept and increasing the level of detail in your prototype.
5. User testing
You have a design - now, it's time to put it to the test. Usability tests with real users are the optimal way to collect constructive feedback.
6. Iteration
Do you need to make changes based on what your users said? At this stage, you act on user feedback where necessary to build the best product possible.
7. Launch
Congratulations, you've built and tested your product or feature. You're ready to share it with the world and feel confident that your customers will love it.
How to measure the outcome of User-Centered Design
So, you and your team are living and breathing human-centered design. You know your customers' needs inside and out, and you're fairly confident you're doing a great job. How do you know for sure if your new, customer-centric approach is working?
Any new feature is expected to create value - for the user and your business. Identify correct qualitative and quantitative signals before launching the feature so you know what to track and measure the outcome.
If you solve a genuine problem for your customers, your data will reflect this. So, what should you be looking for? You need to pay attention to two sets of metrics: product metrics and business metrics.
Product metrics refer to KPIs around usability, such as task success rate and time on task. In other words, is the feature helping users accomplish their goals, promptly? Are they able to find what they are looking for using the navigation instead of relying on search?
Overall business metrics include the adoption rate of the feature and its financial impact, customer retention, and customer satisfaction.
Google Heart Framework
If you don't have specific business and product metrics in place yet, the HEART framework designed by Google's research team is a great place to start.
The HEART framework is a carefully selected set of usability and business metrics that enables you to measure user experience on a larger scale. Its purpose is to guide your decision-making in the product development process.
There are five metrics used in the HEART framework:
Happiness: user attitudes and level of satisfaction
Engagement: how much a user interacts with a product
Adoption: how many new users you have acquired over a specific time-frame
Retention: how good you are at keeping your existing users
Task Success: % of completions of a specific goal such as checkout or registration
How to measure
At this point, you should understand which metrics are needed to measure the success of your User Centered Design strategy. In practice, however, getting the data you need can be challenging.
Small start-ups can easily stay close to the customer and ask them about their priorities and experiences, but it gets more complicated as businesses scale. Recommended best practices include remote usability testing, benchmarking studies, and usability tools such as UXCam.
What else do you need to know about User-Centered Design?
User-Centered Design means taking into account the user's objectives, requirements, and feedback on the product. However, these are constantly evolving as society and user habits change. This is why User-Centered Design is an ongoing cycle with multiple iterations.
You need to keep a close eye on user behavior and continuously adapt and optimize your product. It is not enough to launch a new feature and review the impact one time.
Of course, this is more effort than the "ship it and forget it" approach many businesses today have. We get it - there are always new projects, new goals, new management changes, and too little time to get it all done. However, the business results are worth it.
According to Forrester and Adobe, brands that prioritize user experience see over 1.5x higher YoY growth in customer retention, repeat purchase rates, and customer lifetime value.
From food delivery to automobiles, top brands like Costa Coffee, Ford, Orange, and Vodafone rely on UXCam to understand user needs and monitor user behavior. These insights enable them to deliver first-class products worthy of a globally-renowned brand.
Book a FREE demo today to find out how UXCam can help you understand your users on a whole new level, identify user problems, and build products your customers love.
We hope you found this guide helpful and wish you all the best on your user experience design journey. We are confident that this UCD approach will enable your business to understand customer needs, build awesome products, and be more profitable.
You might also be interested in these;
Best behavioral analytics tools to optimize mobile app UX
20+ powerful UX statistics to impress stakeholders
Mobile UX design: The complete expert guide
5 Best User Journey Mapping Tools
App user journey: Mapping from download to daily use
AUTHOR

Marilyn Wilkinson
Marilyn Wilkinson is a digital marketing strategist and copywriter who works with a number of B2B tech and SaaS brands, including UXCam. She is passionate about awesome user experience, great content, hiking through the mountains and drinking too much coffee.
What’s UXCam?
Related articles
Product best practices
Como Encontrar Usuários Ativos De Um Aplicativo
Descubra estratégias comprovadas para identificar e engajar usuários ativos do seu app, aumentar a retenção, impulsionar o crescimento e maximizar o sucesso do seu...

Tope Longe
Growth Marketing Manager
Product best practices
Product Performance Analysis - A 7-Step Playbook with UXCam
Learn how to use product performance analysis to improve UX, boost retention, and drive growth with actionable steps and...

Tope Longe
Growth Marketing Manager
Product best practices
How to Increase Mobile App Engagement (10 Key Strategies)
Discover the top strategies for increasing mobile app engagement and user retention. From push notifications to app gamification, our expert tips will help you boost...

Tope Longe
Growth Marketing Manager
