What is UX Analytics?
What would happen if you stopped listening to feedback?
You will stop improving and get stuck in the same way of thinking.
Well, the same thing happens if you don’t analyze your UX (User Experience). You are ignoring the real-time feedback from your users!
This guide explains what is UX analytics is, why it matters, and how teams can use it to improve app and web experiences. It also reviews the top tools, including UXCam, Mixpanel, and Hotjar. We also cover best practices, common challenges, and how to overcome them.
Summary - User experience analytics
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is user experience analytics? | It's tracking and analyzing user behavior to improve your app or website experience. |
| Why is UX analytics important? | It identifies issues, optimizes journeys, and boosts satisfaction, retention, and conversions. |
| What tool is best for UX analytics? | UXCam is ideal for mobile apps with features like session replays, heatmaps, and funnel analytics to optimize user experiences |
| How do you start? | Set goals, choose a tool, integrate it, and track metrics like engagement and drop-offs. |
| What should you measure? | Key metrics include session duration, bounce rate, user flows, and conversion points. |
| How do you use the data? | Identify issues, test solutions, and prioritize updates for a better user experience. |
| How does it benefit your business? | Better UX increases retention, conversions, and customer loyalty, driving growth. |
| Is UX analytics only for designers? | No, it helps product managers, marketers, and developers make informed decisions. |
| How do you ensure user privacy? | Anonymize data, get user consent, and follow rules like GDPR and CCPA. |
| What challenges might you face? | Common challenges include fragmented data, interpreting insights, and balancing privacy. Prepare ahead. |
What is UX analytics?
UX analytics is the process of collecting and analyzing data about how people use a digital product. It combines two types of information:
Quantitative data such as clicks, conversions, session lengths, and retention rates.
Qualitative data such as heatmaps, session recordings, and feedback that show how users feel and behave.
Together, these data types help teams understand the “why” behind user actions. While traditional web analytics focuses on page views and traffic, UX analytics goes deeper by revealing how design, layout, and flow affect user success.
With modern tools like UXCam, teams can track events automatically, replay real user sessions, and find issues without adding complex code. The result is a complete view of behavior that helps product managers, designers, and developers make faster, data-informed decisions.
Why is UX analytics important?
Identify friction early: Fine confusing user flows and fix them before they affect more users.
Boost conversions: Pinpoint exactly where users drop off and optimize those moments to increase completion rates.
Drive retention: Discover which features encourage users to return and build on what keeps them engaged.
Prioritize with confidence: Make product changes backed by real data instead of assumptions.
Accelerate debugging: Combine performance metrics with session recordings to uncover and resolve issues faster.
Protect user trust: Ensure compliance and safeguard data with robust privacy and security controls.
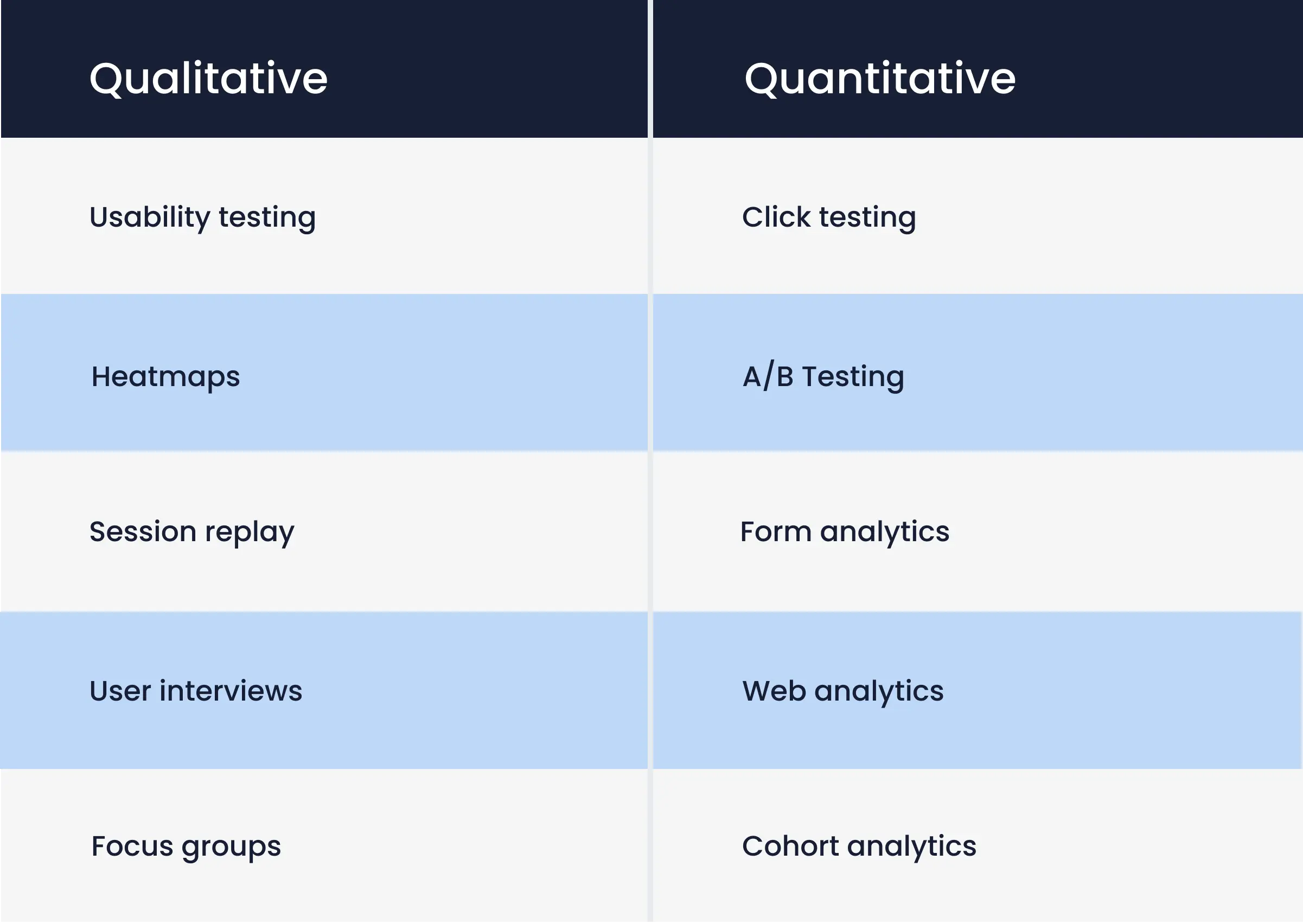
Quantitative vs qualitative UX data
First, we have to distinguish between quantitative and qualitative UX analytics. Quantitative data gives you measurable patterns, while qualitative data explains human behavior.
You need both to improve user experiences.

Quantitative UX analytics measures what happens, clicks, conversions, active users, time spent.
Qualitative UX analytics explains why it happens, confusion, hesitation, or friction points visible in replays or heatmaps.
Modern UX analytics tools, including UXCam, combine both in one dashboard, removing the need to switch between multiple platforms.
Qualitative methods of UX analysis
Usability testing
Usability testing is straightforward: You assess the UX of your product by testing it on users. You do not ask for the users’ opinions, though. Instead, you observe systematically.
There are two main variations of usability testing:
Hallway testing: You ask strangers
Expert review: You bring in experts in the field (for example, students for testing an app for students)
Usability testing helps you identify and address potential issues before a product launch. It allows teams to evaluate overall performance, determine whether participants can complete specific tasks successfully, and measure how long it takes to complete those tasks. Here’s our list of 5 usability testing tools to help you get started.
Session replay
UX testing is great, but there are several issues:
Time: You will spend more time to plan and execute a usability test
Participants: You need to find fitting participants and pay them
Cost: You need professional equipment to conduct a good observation
Session replay is a cost and time-efficient alternative that is easily performed on a daily or weekly basis.
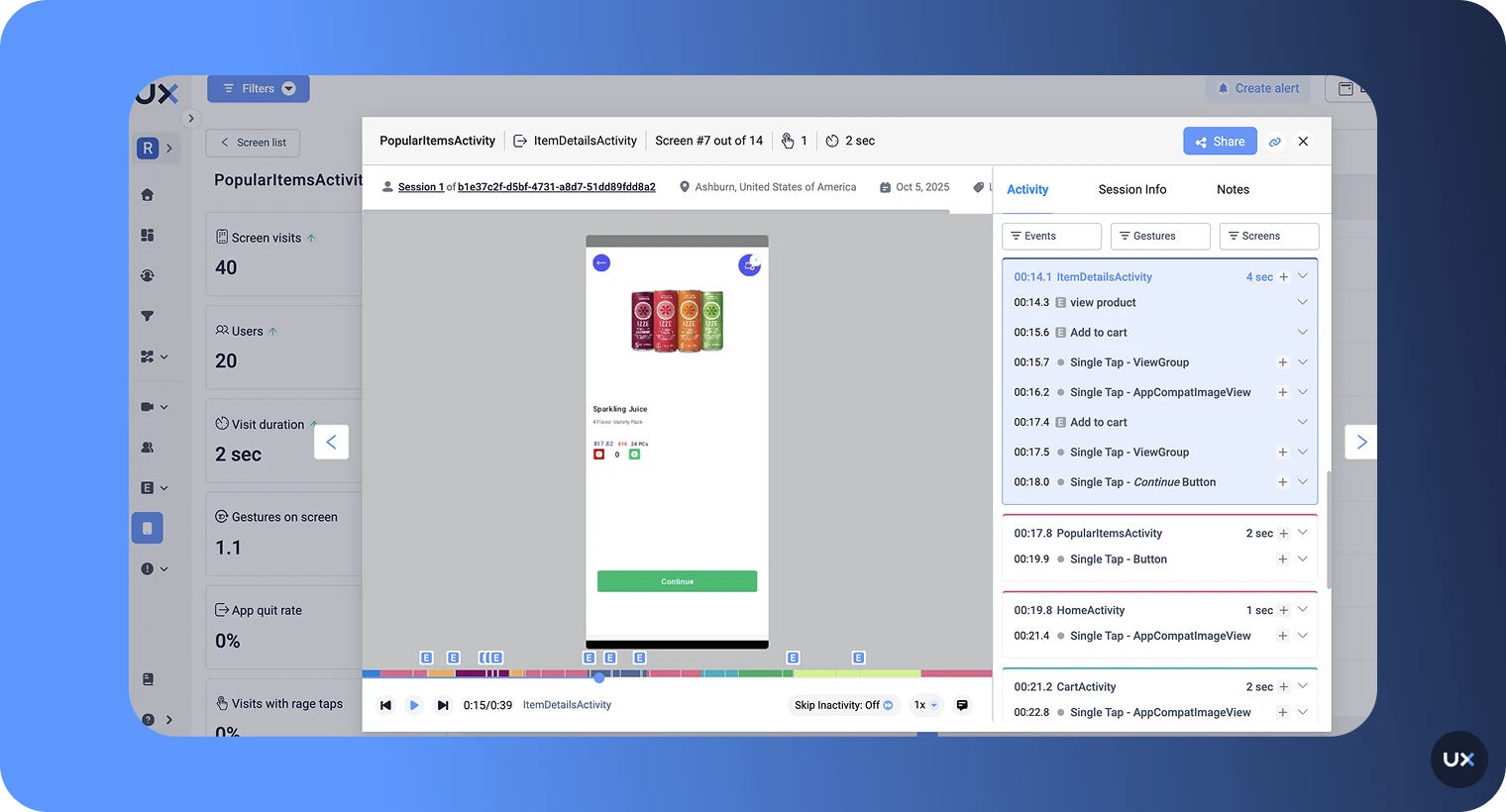
With session replay, you can record and replay videos of real user sessions. You can review the whole user journey, including touch interactions and time spent on each screen. While Usability testing provides you with more details, Session replay has the benefit of observing your users in a natural setting. Learn more about mobile session recording and website session recording in these detailed guides.
Focus groups
Focus groups usually comprise a small group of ~6-10 people. After using your product, the group gets together to discuss the issues and benefits of your UX.
A moderator leads the discussion. You will need a good moderator because it is hard to determine if a discussion makes sense.
Sometimes a point that appears to be irrelevant on the surface might prove valuable if you analyze it afterward. After the discussion, you will need to create a report and evaluate it.
Diary studies
As the name suggests, diary studies collect information by having participants write entries every day.
That has the advantage that there is a longer time frame involved; you are not just limited to one session.
However, diary studies have a tendency to be inaccurate. This is because of the low control of participants and the nature of recalling events. I think Session Replay is the best alternative here.
User feedback
Chances are that you are using this already. You are already receiving e-mails and comments that give you feedback on your product. This feedback is valuable as it comes from your core users.
However, with a business operating at a medium or large scale, it is hard to take all feedback into consideration. It is also hard to centralize this feedback, especially if you get dozens of comments per day.
Heatmap UX research
Heatmaps visualize your user’s actions by overlaying colors. The “hotter” (redder) the color, the more interaction.
Heatmaps are popular because they are easy and fast to understand due to their visual presentation.
Here is an example of a use case:


You can instantly see that most users are logging in via Facebook. Now you can use that knowledge and move the FB button to the top to improve your UX. Heatmaps are especially helpful in testing your most important button: CTA (Call to Action).
Quantitative methods of UX analysis
Web analytics
With web analytics, you can view every type of data you can imagine, as long as it is expressed in charts or numbers. You can track views, clicks, active users, etc. With most tools, you can even set your own metrics.
You should always look to be using one web analytics tool, I am recommending Google Analytics for website traffic data and UXCam for which elements users interact in your web app.
Form analytics
Form analytics is, as the name suggests, conducted in forms. It is a direct way to ask users for feedback and express it in numbers, making the results easy to test.
For example: “How easy do you find it to navigate through our app from a scale from 1 to 10?”
However, there is a thin line: You can annoy your users by asking for feedback all the time. Ironically, using this UX analytics might lead to a worse UX.
A/B testing
A/B testing is an industry standard.
Let’s say you are undecided on what is the best way to proceed with a screen, so you implement two versions of what you want to test (Layout, button colors, etc.).
Afterward, you check which version had the best conversion rate and where the user stayed the longest. Now you have an empirically proven result that shows you the better version.
However, this form of analytics only works if you already have a large number of users. As a rule of thumb, the data only gets relevant after being tested with at least 2000 users.
If you have a mobile app and want to learn about A/B testing tools, check out our detailed review on the best A/B testing tools for mobile apps.
Click testing
Click testing shows what part of the screen users clicks on first or what sequence they are using. You should track each click and the time it takes the user to make the click.
This way, you can find out what click-path your users take intuitively.
How to implement a UX analytics strategy
Starting your own UX analytics strategy to align your product more closely with user needs and preferences will contribute to optimizing business performance.
Here are some quick pointers to consider when getting started:
Define goals and objectives: Clearly describe what you hope to achieve with UX analytics. Outline measurable goals to align with enhancing UX and execute business objectives.
Identify key metrics and data sources: Decide which UX metrics are most relevant to your goals:
Quantitative data like page views, bounce rates, and conversion rates, or qualitative data like user feedback, surveys, and usability testing.
Choose the right tools and techniques: For alignment with your data collection requirements.
Apply data collection methods: Set up the necessary tracking systems to collect user data. Platforms like UXCam implement strict data security to reduce the risk of data mishandling or unauthorized access.
Analyze and interpret the data: Regularly review the collected data to retrieve meaningful insights. Synthesize quantitative and qualitative data to identify patterns, trends, and areas for improvement.
Implement changes, then test: After translating your insights into actionable steps—which some tools will do automatically for you, implement the priority changes or optimizations with the most impact on improving user experiences. Conduct usability tests to validate changes and measure impact on UX.
Then, you just have to continuously monitor the performance of changes. Assess your users' behavior using ongoing analytics and iterate designs or features for more UX enhancement.
| Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
| Data fragmentation | Use centralized tools and APIs to integrate data from multiple sources. |
| Interpreting qualitative data | Apply structured frameworks, segmentation, and collaborate with UX experts. |
| Lack of actionable insights | Align data collection with clear objectives and prioritize impactful insights. |
| Privacy concerns | Follow regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA), anonymize data, and ensure user consent. |
| Complex user journeys | Use journey mapping tools, visual aids, and user interviews to clarify touchpoints. |
| Limited resources | Focus on training, cost-effective tools, and prioritize impactful metrics. |
| Overemphasis on metrics | Combine qualitative and quantitative data for a more meaningful analysis. |
Future trends in user experience analytics
So, what’s next for UX Analytics?
Well, the field is certainly poised for significant advancements, driven by emerging tech and evolving user behavior.
Here are some emerging technologies that will impact UX analytics:
AI and machine learning: AI and ML will play a significant role in analyzing lots of user data more efficiently. AI algorithms that can anticipate user preferences and behavior will enable personalized user experiences and predictive analysis. For example, UXCam’s Smart Events feature automatically recommends interesting events for you to track and helps you set up tracking with a single click. Tara AI, UXCam's AI Analyst watches sessions for you and provide you most important insights while saving you hours.
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR): These technologies will change UX analytics through immersive experiences. Analyzing user behavior in these environments will require new methodologies to learn how users interact with virtual elements.
Conversational analytics: Due to the rise of chatbots and voice interfaces, conversational analytics will become key. Insights from user interactions and sentiments during voice or text-based conversations analysis will improve conversational UX.
Internet of things (IoT) integration: As IoT devices become more common, UX analytics will expand to involve data from interconnected devices. Therefore, user insights will include analyzing interactions with smart home devices and IoT ecosystems.
And here are some of our projections for the future of UX analytics:
Emphasis on emotional analytics: Designs focused on evoking positive emotional responses will be driven by understanding how people feel during interactions. Machine learning algorithms will be used to identify sentiment from voice and text analytics.
Real-time analytics and personalization: Personalization will become more polished through tailored experiences based on real-time interaction analysis.
Integration of behavioral biometrics: Adding behavioral biometrics like typing patterns and gesture recognition into UX analytics to offer more insights into behavior for authentication.
Quantum computing for complex analysis: As quantum computing grows more sophisticated, it will accommodate more complex and speedy analysis of large datasets. This will lead to deeper insights and more accuracy in predictive models in UX analytics.
9 Best UX analytics tools in 2026
Doing UX Analytics gets quite easy using the tools that are available online. There are dozens of user experience analytics tools out there; here are Nine (9) of the best UX analytics software to consider:
Best Quantitative UX analytics software
Google Analytics / Firebase
UXCam
Mixpanel
Amplitude
Adobe Analytics
Contentsquare
Best Qualitative UX analytics software
UXCam
Hotjar (website only)
Glassbox
Mouseflow (website only)
Read our in-depth review of the best UX analytics tools here.
Just to give you a quick example of how useful a combination can be:
Let’s say you have an product.
By using Amplitude, you notice that there are more active users on the iPhone than on Android devices – even though you have the same number of downloads in the app and play store.
Next, you open UXCam to check how users behave on android devices. By going through session replays, you will notice that your app is not optimized for several popular Android devices.
Now you can fix the problem.
It can be easy to get overwhelmed by the number of methods that present themselves to start with your UX Research. In the following, they will be broken down.
This table distinguishes between methods of quantitative and qualitative UX analytics:

Below are the top UX analytics platforms that help you measure and improve user experience.
1. UXCam
UXCam stands out as the most comprehensive UX analytics tool for teams that want to truly understand how users experience their products. It combines qualitative and quantitative analytics into one powerful platform, helping you see not only what users do, but why they do it. Product, UX, and engineering teams use it to identify friction points, optimize user flows, and improve product performance without guesswork.
Key features
Session replay & heatmaps: Watch real user sessions and visualize interaction patterns to uncover UX issues.
Funnel & retention analytics: See exactly where users drop off and which experiences drive engagement.
AI-powered Tara assistant: Instantly summarize behavioral patterns and detect usability problems.
Smart segmentation: Filter users by behavior, device, OS version, or cohort for precise insights.
Issue analytics: Detect rage taps, crashes, and UI freezes linked directly to user sessions.
Autocapture SDK: Automatically track all events, no manual setup or engineering work.
Cross-platform analytics: Unified dashboards for web, mobile, and hybrid frameworks.
Privacy-first design: GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA-compliant with full data masking and encryption.
Pricing
UXCam offers a free plan that includes up to 3,000 sessions per month. Paid plans are customized by session volume and features. Contact us for a personalized quote.
2. Firebase Analytics
Firebase Analytics (part of Google Firebase) is a powerful analytics solution designed for app developers who want a clear view of user behavior, performance, and engagement, all in real time. Built with Google’s infrastructure, it integrates seamlessly with tools like Google Ads, BigQuery, and Crashlytics, making it a go-to choice for teams that want analytics and backend support in one platform.
Key features
Event tracking: Capture user actions such as purchases, sign-ups, or screen visits automatically.
Audience segmentation: Group users by demographics, device type, or behavior for targeted analysis.
Attribution tracking: Measure campaign performance and identify which sources drive installs.
Crashlytics integration: Monitor stability and diagnose crashes in real time.
BigQuery connection: Export and analyze raw event data for advanced reporting.
Pricing
Firebase analytics is free to get started with, but it has a pay-as-you go option.
3. Mixpanel
Mixpanel is a popular product and UX analytics tools for teams that want deep insights into how users interact with their apps or websites. Known for its flexible event-based tracking and intuitive interface, Mixpanel helps product, growth, and marketing teams analyze user behavior in real time, without needing SQL or developer support.
Key features
Event-based tracking: Monitor every user interaction, from clicks to purchases, with customizable event properties.
Funnel analysis: Identify where users drop off and optimize for higher conversion rates.
Cohort and segmentation analysis: Break users into groups by behavior, device, or demographics for targeted insights.
Retention and lifecycle tracking: Measure how often users return and which features drive loyalty.
A/B testing support: Compare feature performance and product experiments in real time.
Pricing
Mixpanel offers a free plan with core analytics and data history, plus its Growth plan that starts at $0.28 per 1k events, and Enterprise tiers with advanced features, larger data limits, and custom pricing options.
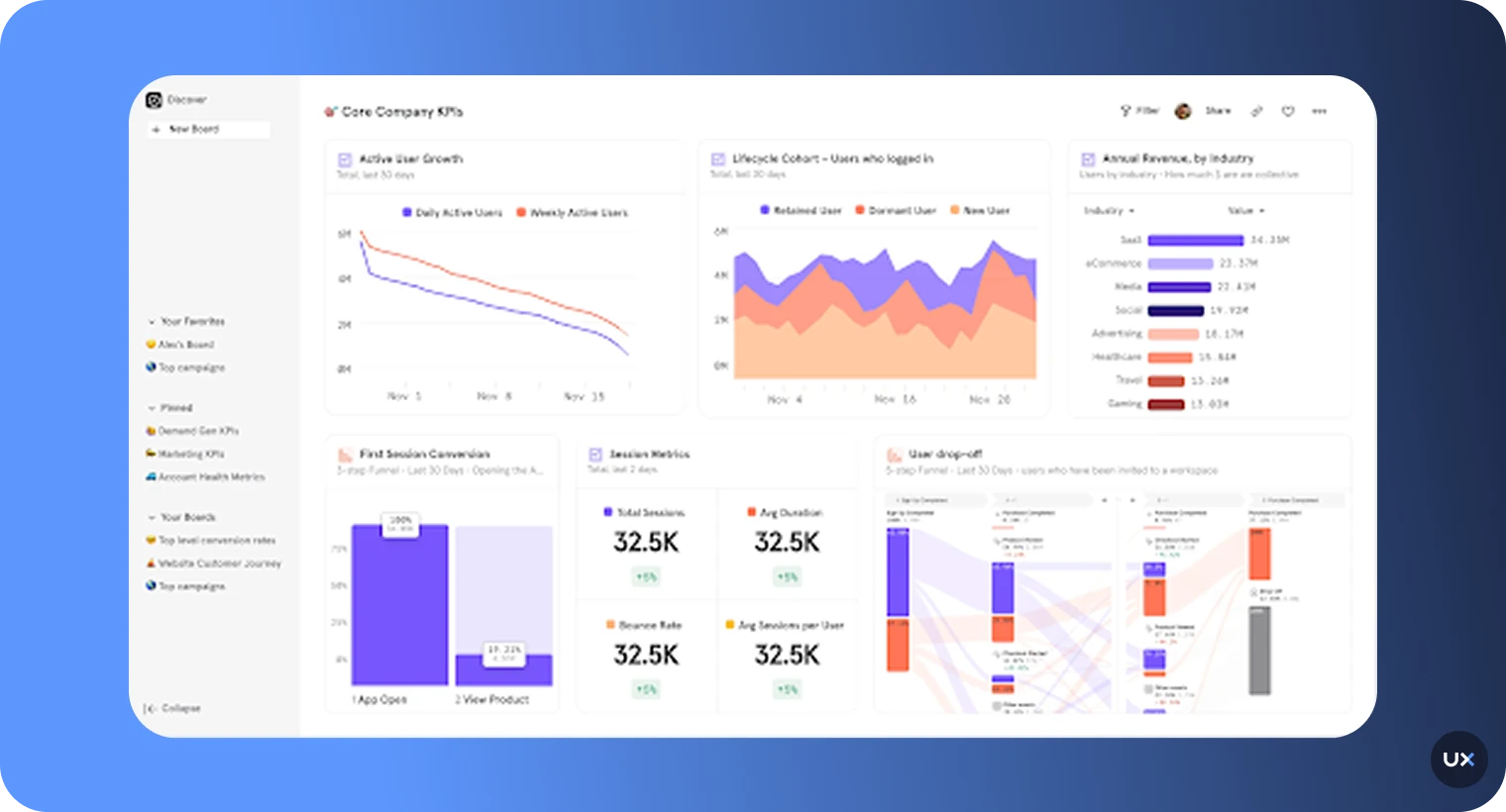
4. Amplitude
Amplitude is a leading product analytics platform built for teams that want to deeply understand user behavior, retention, and conversion across their digital products. It helps product managers, data analysts, and growth teams visualize user journeys and identify the factors that drive engagement or churn.
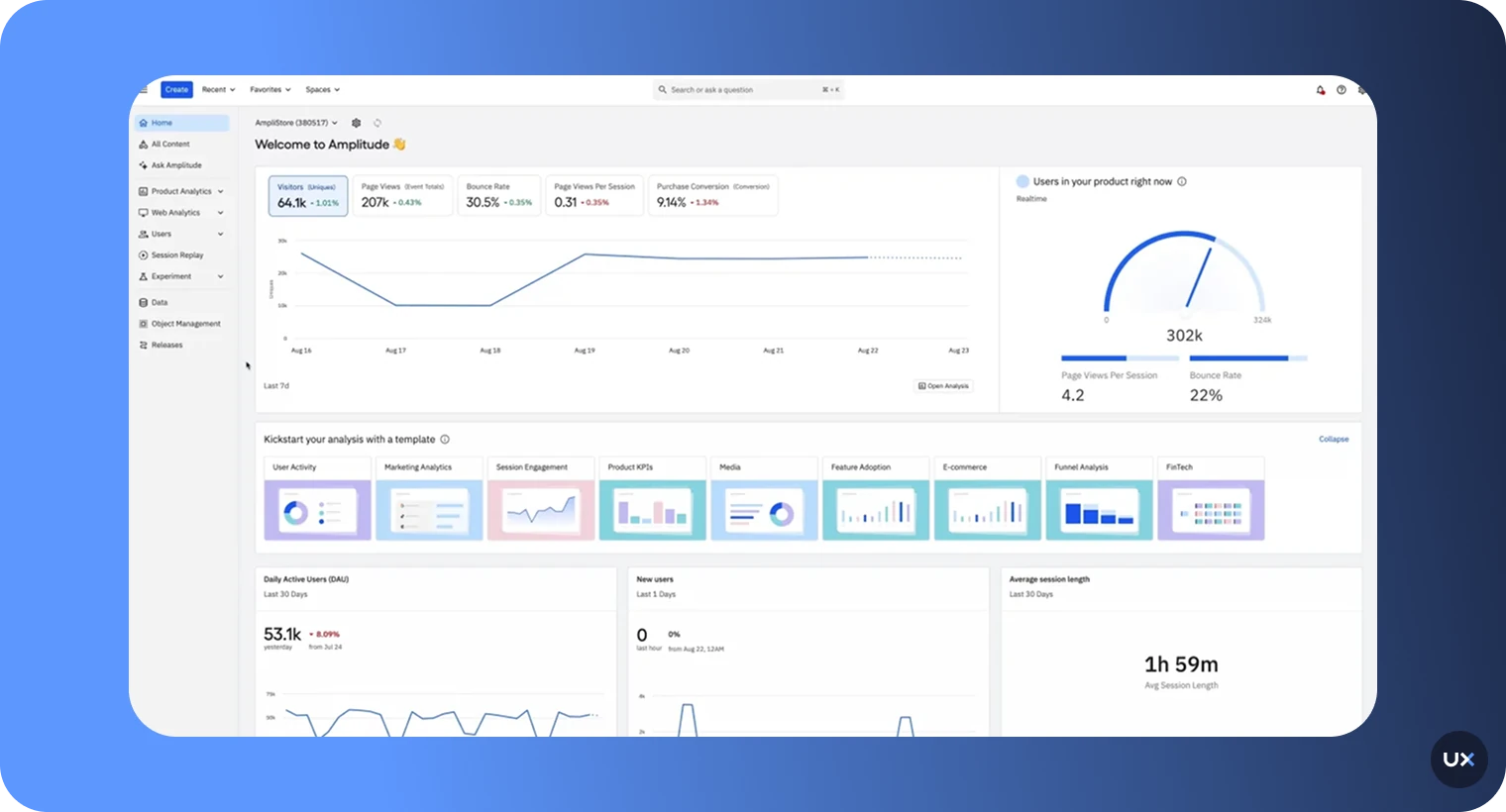
Key features
Behavioral cohort analysis: Group users by shared actions to analyze engagement, retention, and revenue patterns.
Pathfinder & journey analysis: Map every user flow to uncover where users drop off or convert.
Predictive analytics: Use AI to forecast churn, engagement, and high-value behavior.
Funnel tracking: Understand how users progress through key stages of your app.
Experimentation tools: Test hypotheses and measure how product changes affect KPIs.
Pricing
Amplitude offers a free plan with up to 10 million monthly events, while paid plans start at around $61 per month. Enterprise pricing is customized based on event volume, data needs, and advanced analytics features.
5. Adobe Analytics
Adobe Analytics is a powerful enterprise analytics platform that helps large organizations track, analyze, and predict customer behavior across mobile, web, and other digital channels. Part of the Adobe Experience Cloud, it’s built for data-heavy teams that need advanced segmentation, attribution modeling, and real-time visualization across millions of data points.
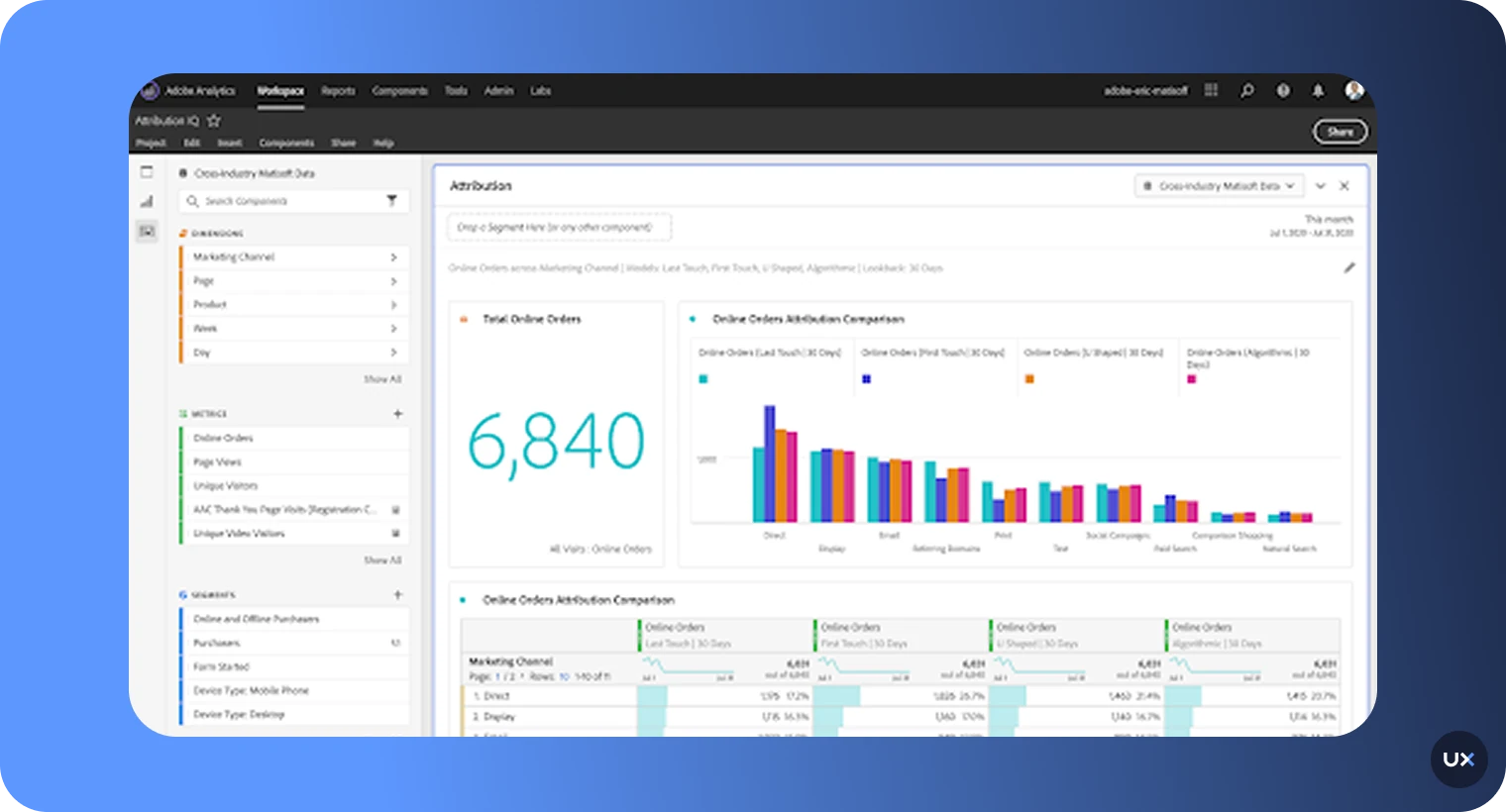
Key features
Advanced segmentation: Create detailed user segments using hundreds of behavioral and demographic variables.
Attribution modeling: Identify which touchpoints and channels contribute most to conversions.
Cross-channel analytics: Track behavior across web, mobile, and offline sources.
Flow and path visualization: See exactly how users navigate through your app or website.
Predictive analytics (Adobe Sensei): AI-powered forecasting and anomaly detection.
Pricing
Adobe offers quote based pricing based on your usage
6. Contentsquare
Contentsquare is a comprehensive digital experience analytics platform designed to help teams understand how users interact with their websites and mobile apps, and more importantly, why. It combines session replays, heatmaps, journey analysis, frustration scoring and AI-driven insights into one unified product, making it a strong choice for UX, product, and growth teams focused on optimizing the full user experience.
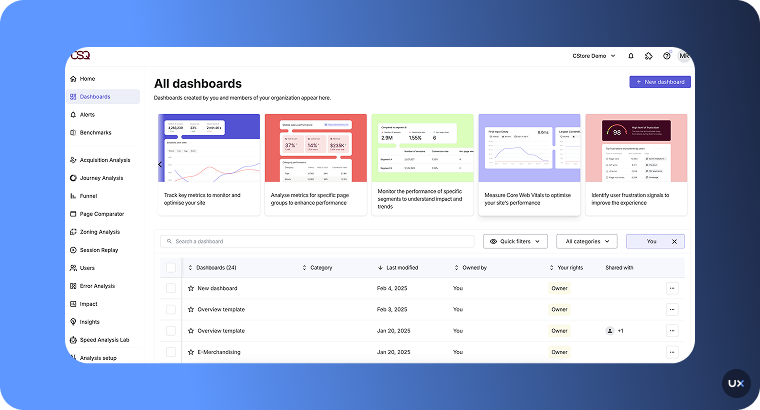
Key features
Session replays: Visualize individual user sessions and see where users click, scroll or hesitate.
Journey mapping & cross-channel analysis: Understand multi-session flows across web, mobile web and apps, showing how users navigate before conversion.
AI-powered insights: Use built-in AI (Sense) to surface key friction points, recommended next actions and summaries of user behavior.
Automatic data capture: Start collecting all user interactions from day one with minimal manual tagging.
Frustration scoring & performance monitoring: Detect rage taps, errors and performance issues that impact UX and conversion.
Pricing
Contentsquare offers custom pricing based on your needs.
7. Hotjar
Hotjar is a widely adopted behavior-and-feedback analytics platform designed to help UX teams, designers, and marketers understand how website visitors behave, engage, and feel about their experience. It combines heatmaps, session recordings, survey tools and user feedback widgets, all geared toward uncovering why users act the way they do.While it’s tailored primarily for websites rather than full mobile/web apps, Hotjar helps teams identify friction, improve conversions, and validate design decisions with qualitative context. It acquired by Contentsquare.
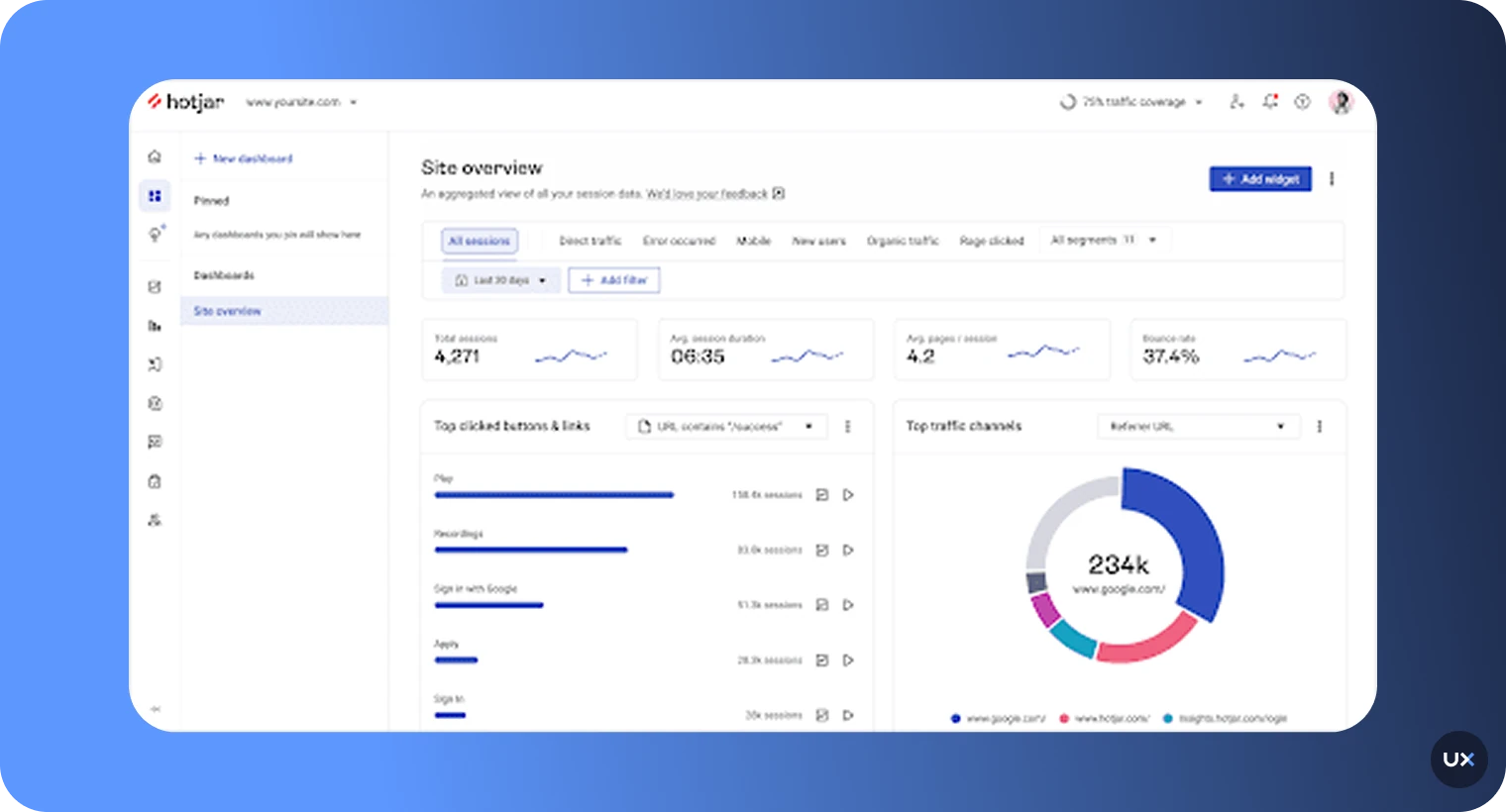
Key features
Heatmaps (click, scroll, move): Visual overlays show where users click, how far they scroll, and where they pause, highlighting attention and neglect zones.
Session recordings: Watch individual user sessions to observe real-time navigation, hesitations, rage clicks and confusion.
Feedback & surveys: On-site polls, NPS prompts, and feedback widgets let you ask users questions and gather contextual sentiment.
Conversion funnels & drop-off tracking: Visualize key user flows and see where visitors abandon or convert.
Team collaboration features: Dashboards, user segments, highlights and sharing tools enable teams to explore insights together.
Pricing
Offers a free forever plan. Paid plan starts at $49 per month
8. Glassbox (previously SessionCam)
SessionCam, acquired by Glassbox in 2020, now operates within the Glassbox platform to deliver a full-fledged digital experience intelligence solution for websites and mobile apps. It captures 100% of user interactions automatically, enabling enterprises to replay sessions, analyze journeys, detect friction points, and link behavior to business outcomes. This tool is tailored for large organizations that need advanced visibility into user behavior across devices and channels, as well as robust compliance and data governance structures.
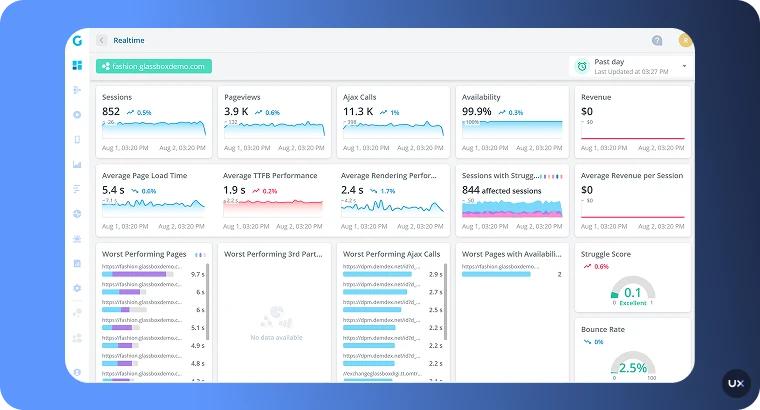
Key features
Session replay & interaction maps: View video-style reconstructions of user journeys, including taps, clicks, scrolls and device changes.
Struggle detection & search-able sessions: Automatically flag sessions with rage clicks, freezes or errors; filter by user ID, browser, or behavior.
Journey & funnel analytics: Map customer flows across web and mobile, identify drop-offs, and visualize full cross-platform experience.
Full-data capture & no sampling: Capture all events in each session, enabling granular retrospective analysis without relying on sampling.
Enterprise-grade security & data governance: ISO/IEC 27001-certified framework, data masking capabilities and flexible data retention policies
Pricing
Glassbox offers custom pricing upon request.
9. Mouseflow
Mouseflow is a web-focused analytics platform designed to help teams understand how visitors navigate their website, uncover friction points, and optimize conversions. With features such as heatmaps, session replays, funnel analytics, and feedback tools, it enables UX and marketing teams to move beyond standard metrics and get visual, contextual insights into user behavior. However, it’s primarily built for web experiences only, which means mobile-app analytics remain limited compared to tools like UXCam.
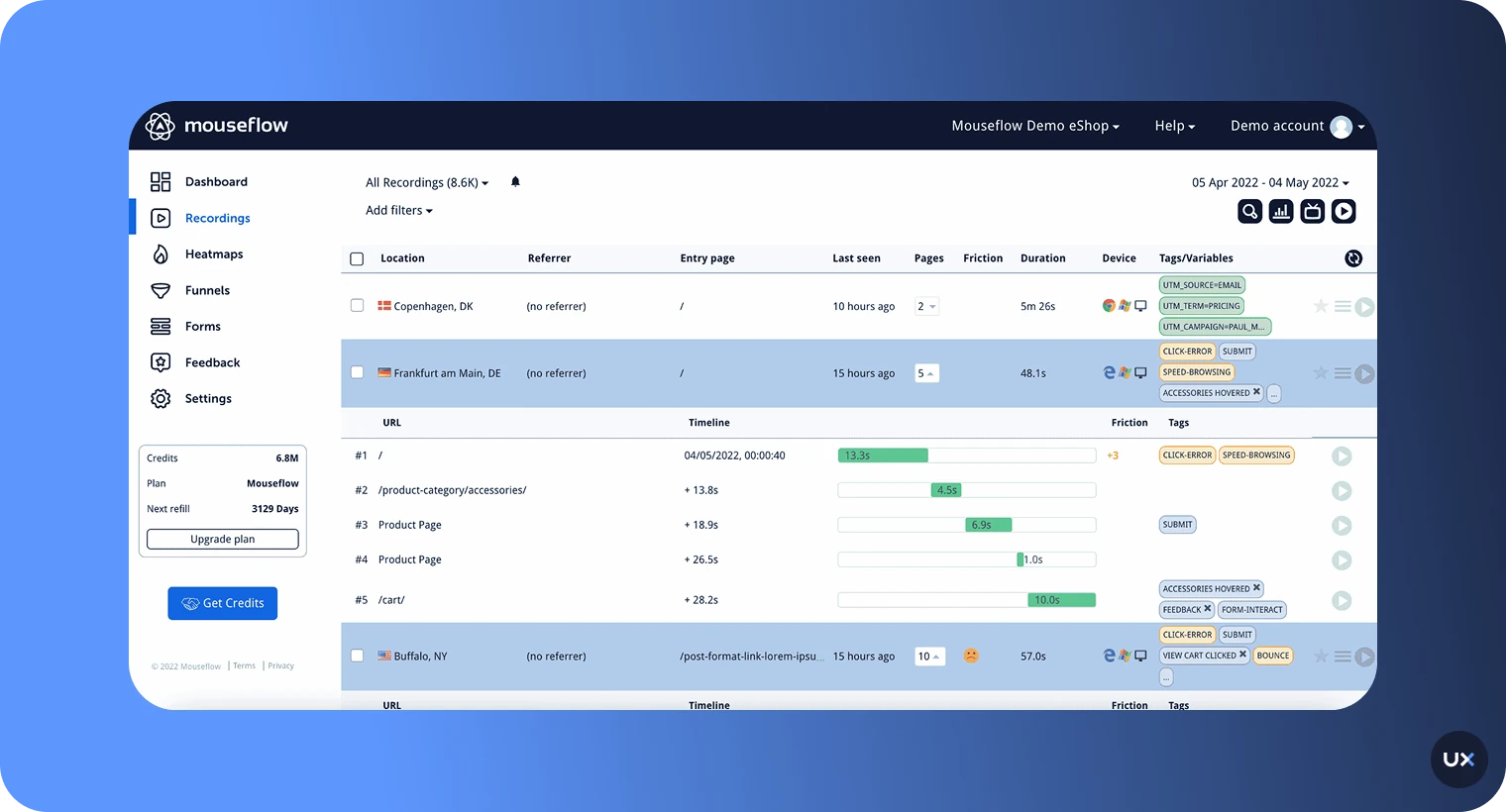
Key features
Session replay: Watch actual visitor journeys to identify navigation issues and behavior patterns.
Heatmaps: Click, scroll, attention, movement, geo-location and interactive heatmaps help visualize engagement zones.
Conversion funnels & form analytics: Map drop-offs through key sequences and optimize forms and checkout flows.
Friction scoring & segmentation: Flag sessions with rage clicks or errors, and segment visitors by behavior, geography, or source.
Feedback and survey tools: Gather direct user sentiment via on-site surveys and feedback widgets.
Pricing
Mouseflow offers a free tier for very limited usage (500 sessions/month). Paid plans start at $39 per month.
Improve your UX analytics with UXCam
UX analytics isn’t just about tracking numbers, it’s about understanding people. With the right insights, you can design smarter products, fix issues faster, and create experiences users love.
UXCam gives you that complete view. From session replays and heatmaps to funnels, AI insights, and frustration tracking, it helps your team see exactly how users experience your app or website, and why they behave the way they do.
Start your free trial today and unlock 3,000 monthly sessions with full access to UXCam’s features. See your product through your users’ eyes, and start turning insights into impact.
You might also be interested in these;
Best behavioral analytics tools to optimize mobile app UX
What is User Behavior Analytics? It's not UX Analytics
20+ Powerful UX Statistics To Impress Stakeholders
Mobile UX Design: The Complete Expert Guide
Best UX Tools for user experience design teams
Best Remote Usability Testing Tools
Top 11 Analytics Tools for Mobile apps
UX audit - A beginner's guide (steps, templates & checklist)
Related articles
UI/UX Design
What is UX Analytics?
UX Analytics helps you to improve your product, thus increasing your conversion rates and...

Jonas Kurzweg
Product Analytics Expert
Product best practices
Gestalt Principles - The Complete Overview
Use the subconscious to create delightful...

Annemarie Bufe
Product Analytics Expert
UI/UX Design
10 Best App Design Practices for App Development in 2025
If you're developing an app, you need to keep UX in mind if you want it to succeed. Check out these 10 best app design...


